![]()
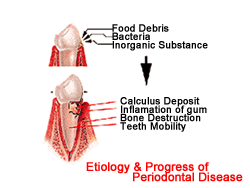
Swollen
and painful gums generally result from periodontal disease.
The structure of a gum tissue consists of gums and alveolar bones. For
young people the inflammation is usually limited to gums, which is called
gingivitis and mostly worsens to the chronic periodontitis that is the
cause of the loss of teeth in later years. Gingivitis can be treated by
scaling at the dental office and healthy gums are fully restored by
regular brushing. On the other hand, chronic periodontitis requires more
complex treatment such as scaling, periodontal curretage (a treatment that
puts inflamed tissues between gums or teeth under anesthesia and then
scrapes them out with a tool) and after the surgery, regular examination
and dental care are also necessary.
Even though patients with severe cases of periodontal diseases can use
some supplementary medications available on the market after the surgery,
taking medicine without a prescription from the dentist is not considered
to be helpful. This does not root out the cause of the disease as well.
Scaling and proper brushing is a much better cure than any other medicine
or food. Once healthy gums are restored, try to take vitamin C or foods
that contain lots of vitamin C.